Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis
Detects possible genetic and/or chromosomal disorders in embryos
Better quality and more chances of implantation
What does Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis detect?
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD or PGT) detects possible genetic and/or chromosomal disorders in embryos obtained during IVF in order to avoid the transmission of hereditary and serious genetic diseases
Do you want us to study your case?
This technique allows the selection of healthy embryos, with better quality and more chances of implantation, increasing the success of IVF treatments and reducing the number of cycles.

What is Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis?
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) allows us to select healthy embryos that do not have specific chromosomal or genetic abnormalities, thus improving the chances of a successful pregnancy and reducing the risk of transmitting hereditary genetic diseases. To carry it out, we perform a biopsy of the embryo’s cells which we analyse before they are transferred to the uterus.
Advantages of performing PGD/PGT
It detects and selects the healthiest embryos, with the best quality that are free of chromosomal and/or genetic alterations.
It avoids the transfer of embryos with anomalies that can cause early miscarriage or health problems for the child.
It puts an end to the transmission of hereditary diseases to future generations.
We avoid transferring embryos that, due to their anomalies, will not implant or will not be able to develop.
We avoid freezing and transferring embryos that are not viable, eliminating the cost of unsuccessful transfers.
PGD guarantees that the embryo is healthy. This reduces the risk of miscarriage and emotional stress for patients.

What information does Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis provide us with?
PGD has been developed to diagnose more than 300 diseases. Using this genetic analysis we can look for the presence of specific chromosomal or genetic abnormalities. This can include the detection of trisomies, monosomies or other genetic alterations that could affect the development of the embryo. Specifically, we are referring to chromosomal abnormalities and monogenic abnormalities:
- Changes in the structure: the chromosome is missing or has a missing or extra part, is on another chromosome or is inverted.
- Alterations in the number of chromosomes: this happens when there are too few or too many chromosomes. For example, trisomy 21, which causes Down’s syndrome, is a chromosomal alteration in which there are three copies of chromosome 21 instead of two. Or, conversely, in Turner syndrome, the female has one chromosome less, the sex chromosome X (karyotype 45, X0).
Anomaly in the number and arrangement of chromosomes in the embryo is the most frequent cause of implantation failure and early miscarriage.
Monogenic alterations are mutations affecting a single gene. These mutations can cause genetic diseases that can be transmitted to offspring, such as cystic fibrosis or haemophilia. They are caused by changes in the DNA sequence of a single gene.
Types de PGD
Preimplantation Genetic Testing includes several types of tests that we use to evaluate different genetic and chromosomal aspects of the embryos:
- DGP-A or aneuploidy screening
This preimplantation genetic diagnosis technique helps us to detect anomalies in the number of chromosomes, that is, chromosomal losses or gains in the embryos, as happens with the trisomy of the 21st pair or Down Syndrome, where instead of two chromosomes there are three.
- Monogenic PGD-M
Focuses on analysing specific genetic mutations, also known as monogenic mutations, which are associated with inherited genetic diseases, such as cystic fibrosis. PGD-M is usually used when there is a history, such as a previous sick child, or where one or both parents are known to be carriers of the same genetic disease and there is a risk of passing it on to their offspring.
- Structural chromosomal PGD-SR

For whom is PGD suitable?
PGD diagnosis is a very useful procedure for any couple undergoing IVF treatment, as the transfer of a healthy embryo reduces the time needed to achieve pregnancy and the number of IVF cycles. However, it is especially recommended for:
Couples with a family history or who have been diagnosed with chromosomal abnormalities.
Repeated miscarriages
Implantation failures in two or more IVF cycles.
Advanced maternal age, over 38 years old.

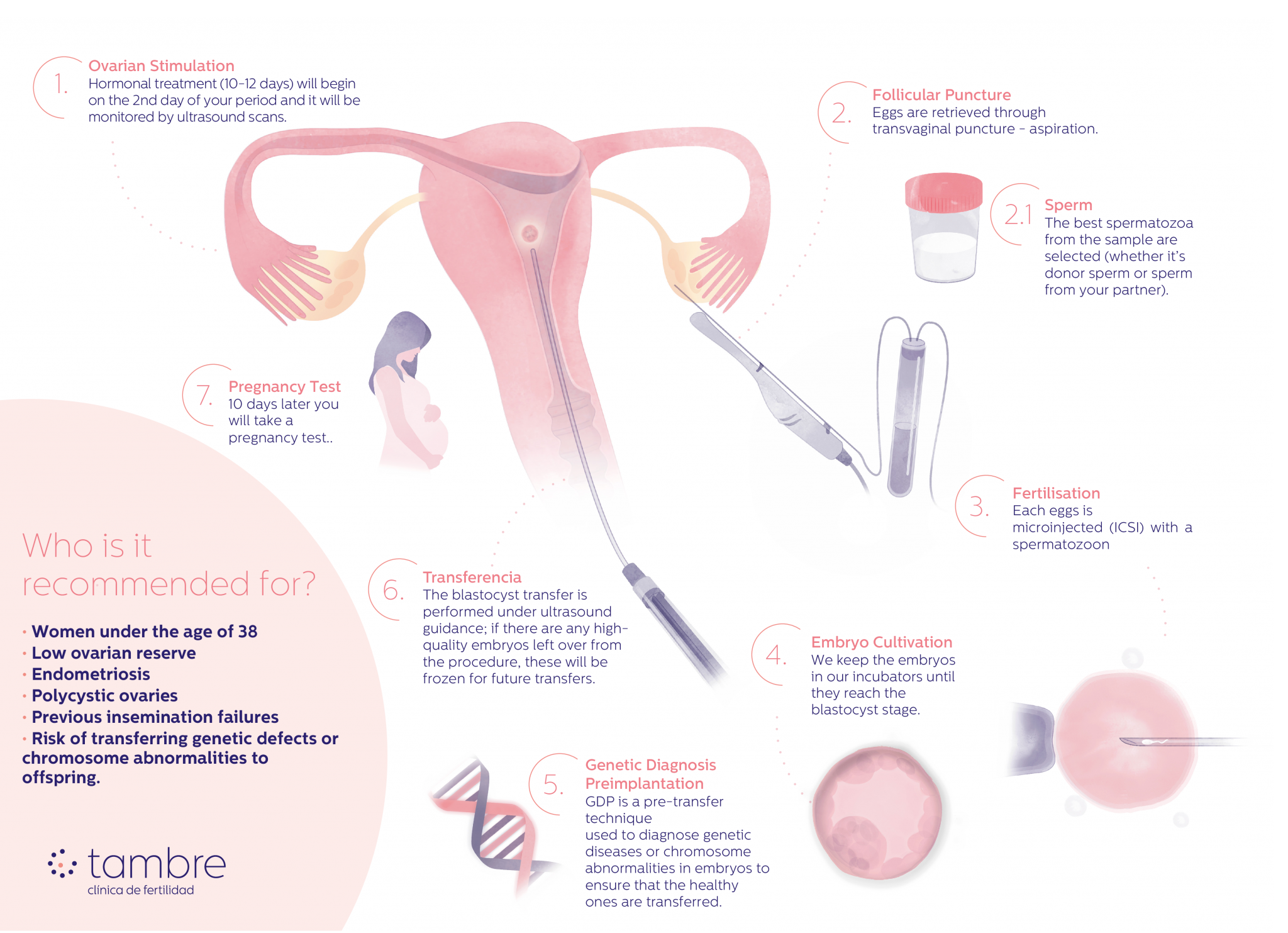
Phases of IVF treatment with PGD
In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF) treatment with Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) involves several phases:
- Personalised ovarian stimulation: from the 2nd day of menstruation, hormonal treatment is started for 10-12 days. During this process, the ovarian response is monitored using ultrasound scans.
- Oocyte collection: When the follicles reach the appropriate size, transvaginal puncture-aspiration is performed to extract the oocytes. This procedure is carried out under anaesthesia with ultrasound monitoring.
2.1-Selection of the best spermatozoa from the couple or the donor. - In vitro fertilisation: The eggs are fertilised in the laboratory with the selected sperm by intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), where a sperm is injected directly into the egg.
- Embryo culture: The resulting embryos are kept in our laboratory incubators until they reach the blastocyst stage.
- Embryo biopsy: Using aspiration with a micropipette, several embryonic cells are extracted.
- Vitrification of the embryos: The embryos are vitrified in our laboratory while awaiting the PGD results.
- Genetic analysis: The biopsied cells are sent to the genetics laboratory to detect genetic/chromosomal abnormalities.
- Endometrial preparation: Once we have the results, we prepare the uterus so that it is in the best conditions to receive the embryo.
- Transfer of embryos: When the endometrium is prepared, the healthy embryos are identified and one of them is selected. It is then thawed and transferred to the mother’s uterus.
- Pregnancy test: 10 days after the transfer (beta wait) a pregnancy test is performed.
Why have Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis at Tambre?
At Tambre we carry out pre-implantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) on embryos in the blastocyst stage, approximately 5 days after fertilisation. We prefer to wait until this period has elapsed because embryos reach a stage at which they have an inner cell mass that will give rise to the foetus and an outer layer that will form the placenta, known as the trophectoderm. At Tambre we perform the biopsy on the outer layer, the trophectoderm in order to avoid damaging or interfering with foetal development.
Before carrying out PGD, it is essential to have a sufficient number of embryos. This helps us to select only those that are of high quality and diagnosed as genetically “normal”. This is why at Tambre we carry out fully personalised ovarian stimulation in order to obtain an adequate number of oocytes.
At Tambre we maintain rigorous quality control throughout the process, ensuring that analysis times and results are optimal and that the embryos are preserved in the best possible conditions.
Thanks to our experience, technology and dedication, at Clinica Tambre we offer exceptional success rates in pre-implantation genetic diagnosis.

IVF-PGD has an 80-90% higher chance of success
Embryos selected by IVF-PGD are 80-90% more likely to implant than without PGD

Specialists in Advanced Reproductive Medicine
45 years of medical excellence.
We design tailor-made treatments
State-of-the-art assisted reproduction laboratory
Our own andrology laboratory.
- RI Witness™ for the safety and traceability of gametes.
- GERI®: Embryo Incubator®.
- Fenomatch, we find the right egg donor and/or sperm donor and match them with you.
- Zymot-ICSI (Chip Fertile), selection of the best sperm before ICSI.
- You will have your own gynaecologist and nurse, except for emergencies, and the same medical team will follow your case in depth and attend you from the beginning to the end of the treatment.
- You will have a consultant from our Specialised Tambre Care team who will support you and answer any question you may have throughout the whole process.
We stay with you
Our support team is always at your side for whatever you need
Shall we call you?
Our support team is always at your side for whatever you need
Or send us an email to atpaciente@clinicatambre.com